Experimental Hydrogeological Park
Like many countries worldwide, India is facing intense pressures on their groundwater resources. An Experimental Hydrogeological Park established in Hyderabad is helping to better understand the impacts on groundwater.

Experimental Hydrogeological Park in Hyderabad, India
Overseen by the Indo-French Centre for Groundwater Research, the Experimental Hydrogeological Park is located in a multi-disciplinary observatory site of the National Geophysical Research Institute.
Extensive monitoring of the crystalline rock aquifers in the Park has been ongoing since 2008. Twenty-six groundwater monitoring wells were constructed between 2008 and 2017. In 2015, an artificial managed aquifer recharge structure was added to observe subsurface flow and water quality impacts.
A hydrodynamic well cluster is used to conduct regular hydraulic investigations, including pumping, slug, and tracer tests. In addition, water level dataloggers continuously record water level fluctuations and manual water level measurements are taken each month.
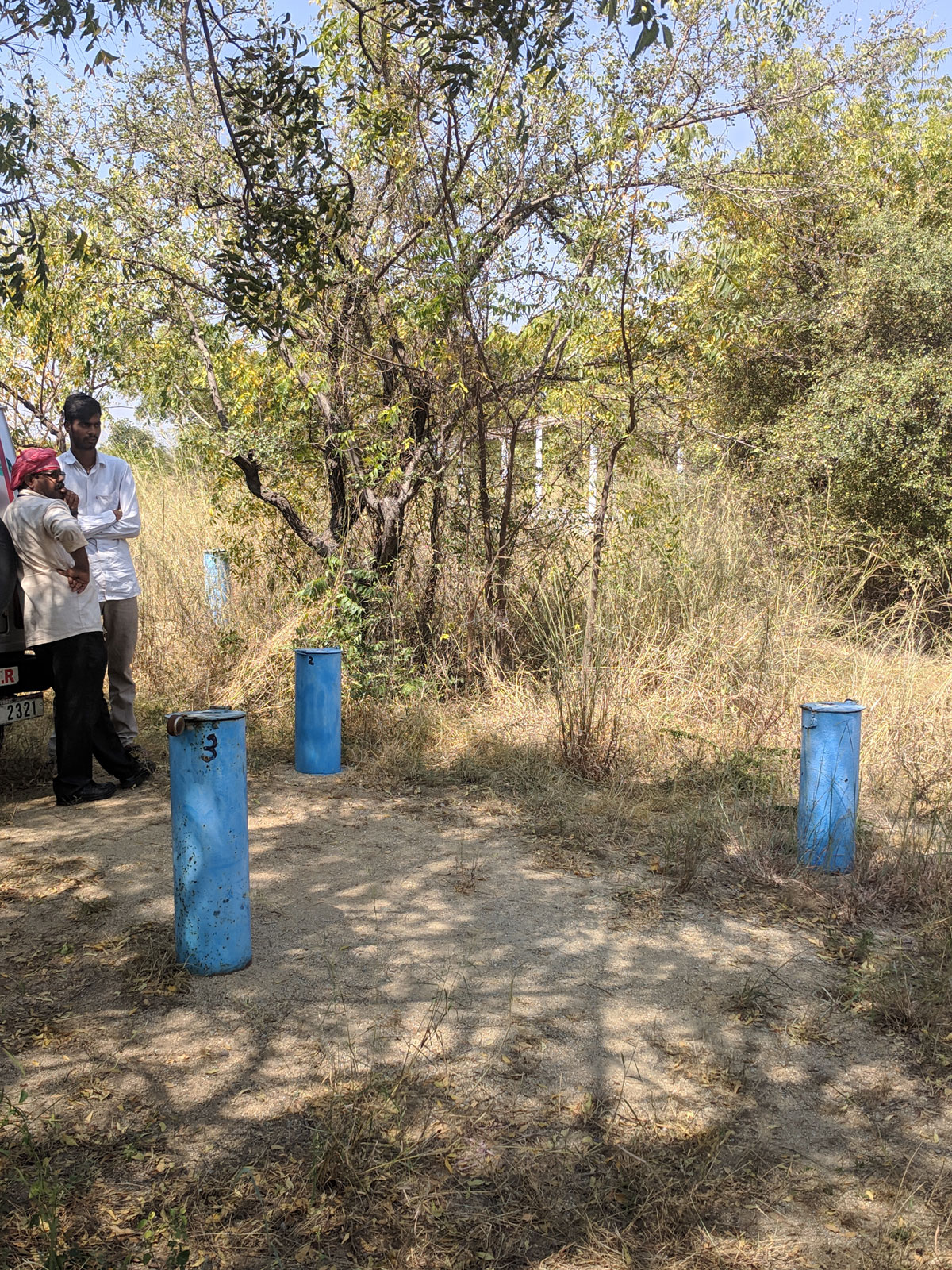

A cluster of groundwater monitoring wells used for hydraulic investigations.
Analyses of aquifer structure, hydrodynamics, and transport processes in the Experimental Hydrogeological Park, aid the overall goal of enhancing the knowledge of complex hydrogeology in the country.
Transient Hydraulic Tomography
Students at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad are taking part in a transient hydraulic tomography project at the Park.
Part of their study includes sequential cross-hole hydraulic tests. Field trials involve slug testing, single hole pumping, and cross-hole pumping tests. To conduct the tests, a number of groundwater monitoring wells are fitted with pneumatic packers to create multiple depth-discrete monitoring zones in each well.
The investigation aims to obtain the spatial distribution of hydraulic parameters (such as hydraulic conductivity and storage) in weathered, fractured granite. The packer test technique is typically successful in a number of geological conditions, and a result will help determine the hydrogeological conditions of this specific environment.
Pneumatic Packer Test Equipment & Training
Recently, Solinst staff visited the site to provide hands-on instruction for the equipment used in the transient hydraulic tomography project.
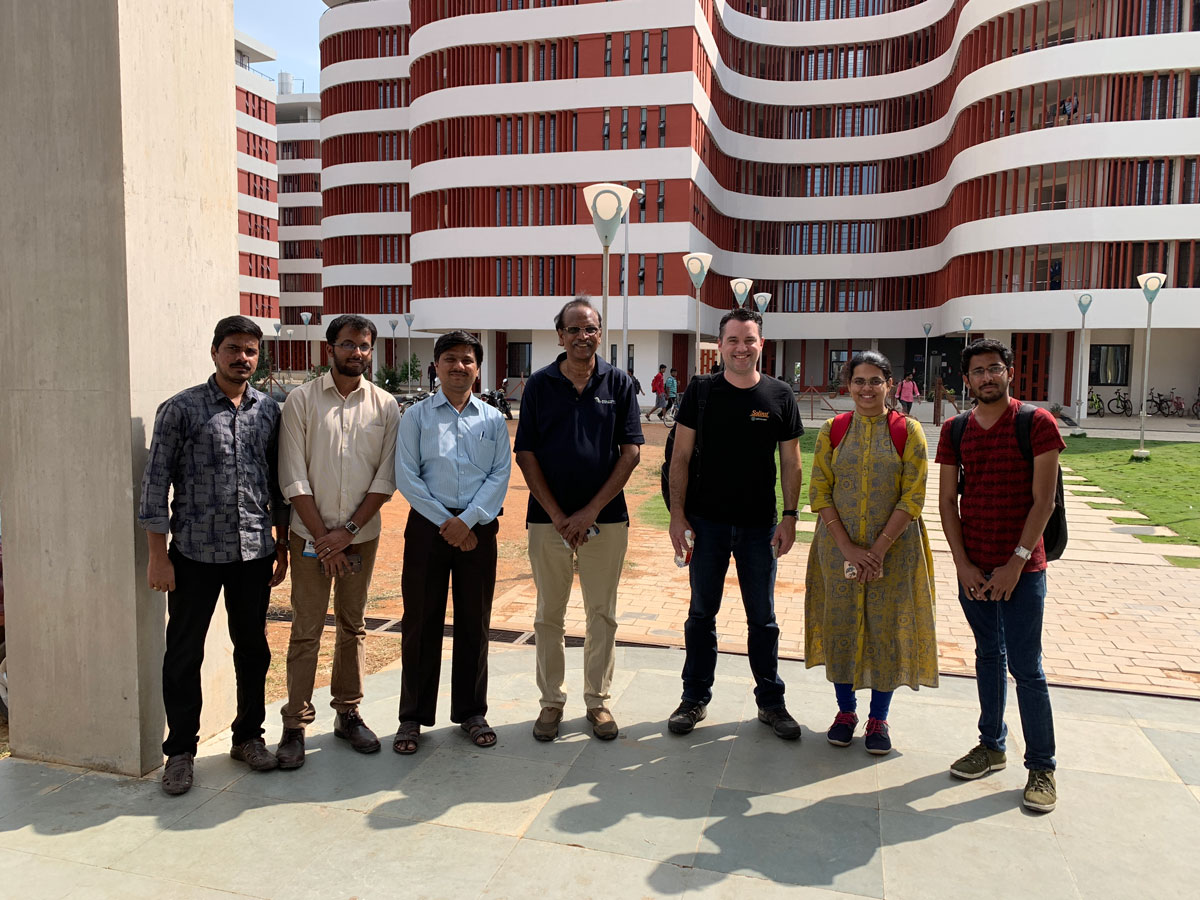

Professor Kandi Sangareddy, students, Solinst distributor and staff at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad.
The project is utilizing the following Solinst instruments:
Model 800 Low Pressure Pneumatic Packers are used to isolate the discrete zones in the groundwater monitoring wells to perform the slug and single hole/cross-hole pumping tests.
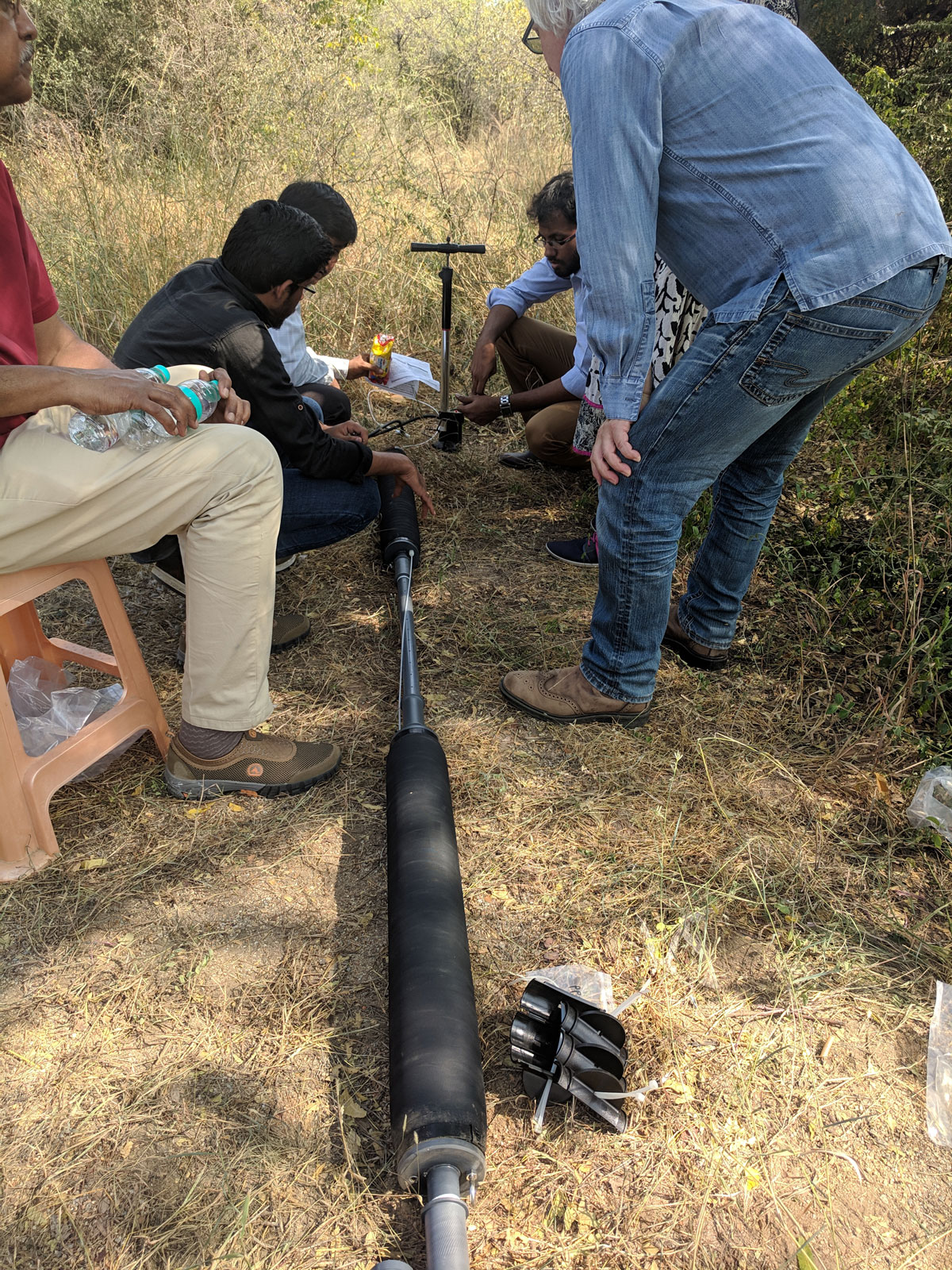

A straddle packer setup for isolating a discrete groundwater monitoring zone.
Model 3001 LTC Levelogger Edge dataloggers are deployed in the wells to monitor water level, temperature, and conductivity (a Barologger Edge provides barometric data for barometric compensation of the water level data).
Model 407 Bladder Pumps and 408 Double Valve Pumps are used for low flow groundwater sampling during tracer and contaminant transport tests. Both Solinst Pneumatic Pumps are controlled using the Model 464 Electronic Control Unit, which automates the pump’s vent and drive cycles. A Solinst 12V Compressor is used to supply air to drive the pumps.
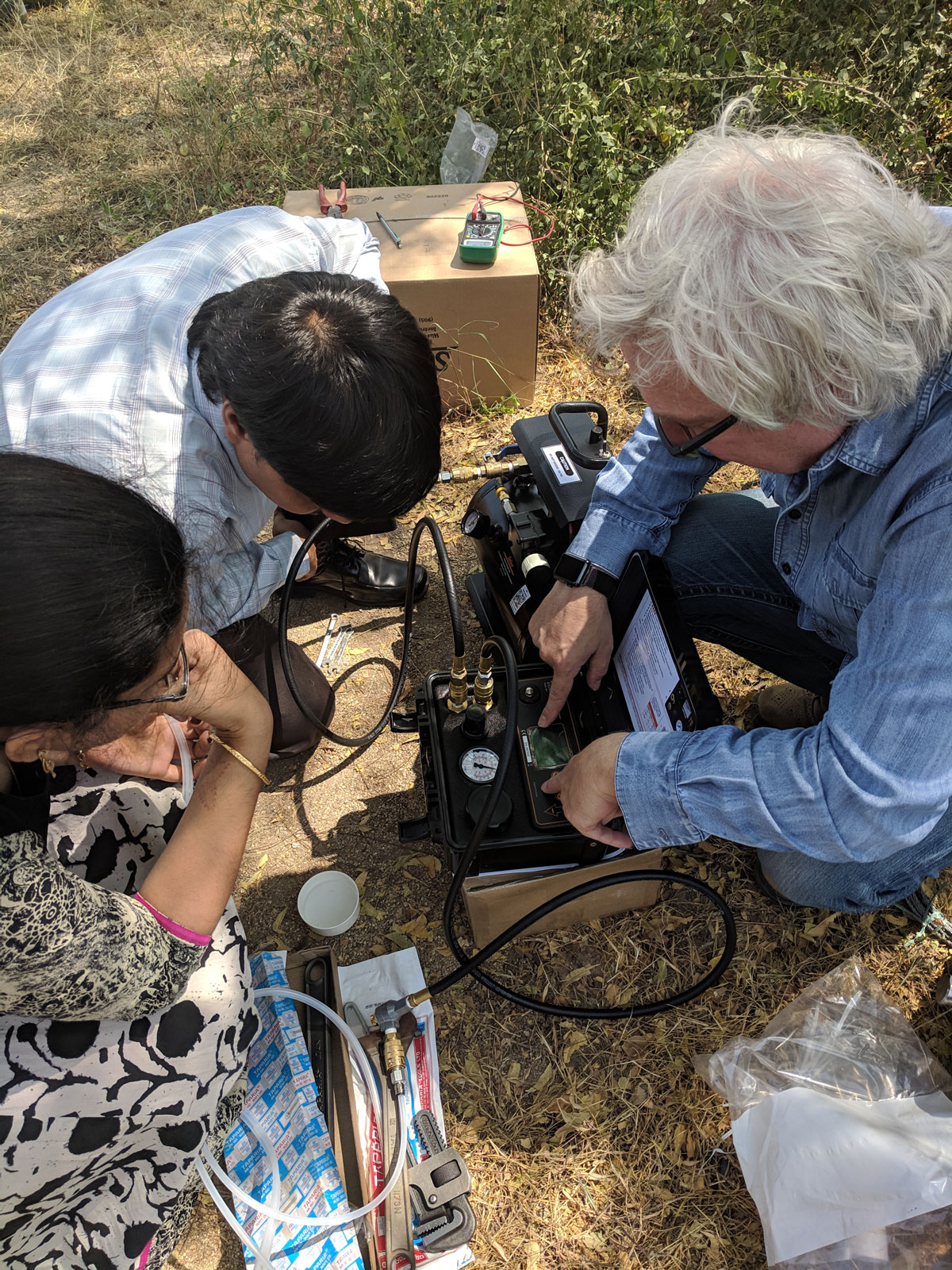

Programming a Model 464 Electronic Pump Control Unit for use with Solinst Pneumatic Groundwater Samplers.
The results of the transient hydraulic tomography project will be compared to laboratory experiment findings and used evaluate the performance of various other models. 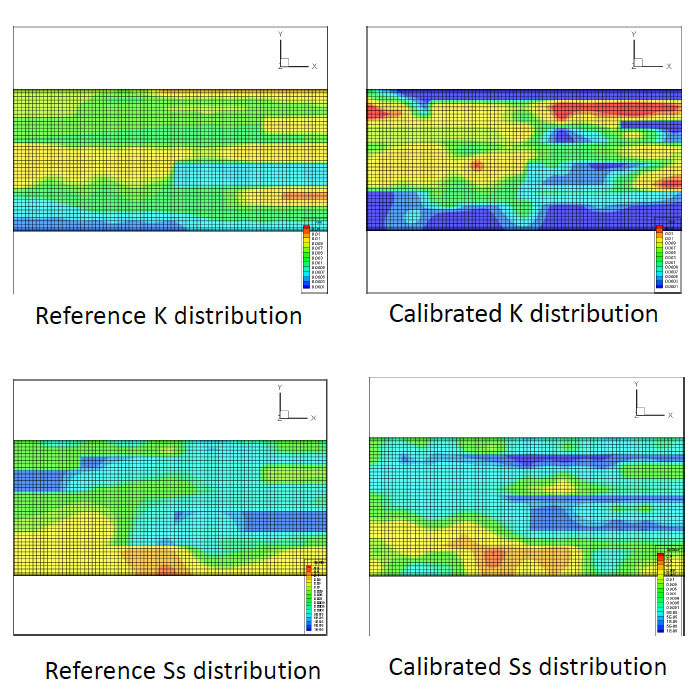
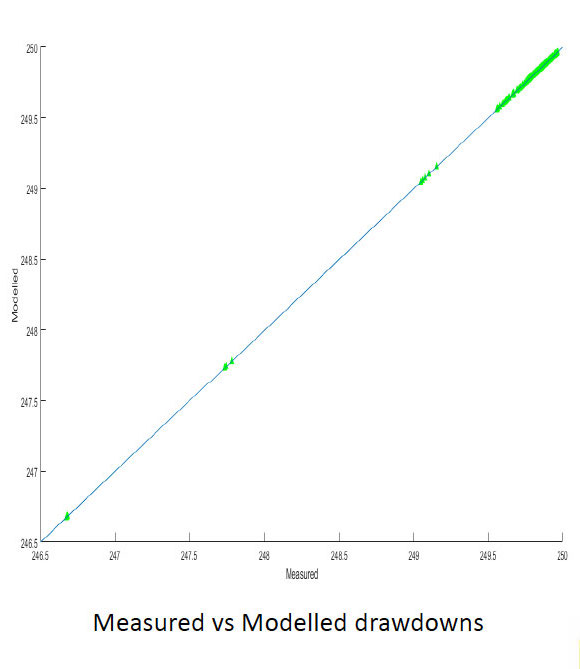
Results from synthetic hydraulic tests.
Overall, the data collected will help map the heterogeneity of hydraulic conductivity and specific storage in the crystalline rock aquifer and determine the location of large fractures and highly conductive zones.
