Why Use Multilevel Monitoring Wells?
Depth Discrete Groundwater Monitoring
Reduce Costs and Field Time
Choosing the Right Monitoring Well
Groundwater. We all recognize it as a necessity and the need to keep watch on its quality and quantity with time. However, how do we effectively monitor something that we can’t see? The short answer – choose the right monitoring wells!
As an environmental colleague working in the industry, your goal is our goal – to select a monitoring well that provides detailed information on hydraulic and transport properties and water chemistry from each geological stratigraphy so changes can be identified over time. You’re looking for cost-efficient, defensible data that’s easy to collect.
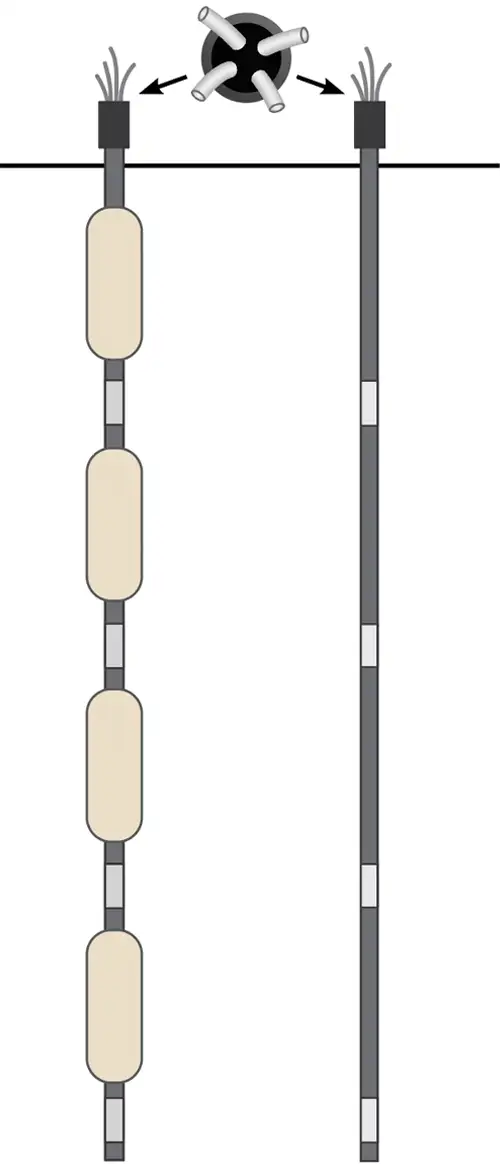
The Multiple Level Well (aka. Multilevel) – what is it?
As pictured, Multilevel monitoring wells use a number of individually isolated short screens to ‘capture’ water at each specific depth in a single borehole. Each well screen is isolated using sequences of clay seals or borehole Packers so that a representative water level and water sample can be collected from multiple depths in a single borehole.
Reasons for Using a Multiple Level Well.
Geology is not always ‘homogeneous’. Understanding the vertical differences in water levels and water chemistry across complex geology is key.

 Well Cluster – Not Ideal
Well Cluster – Not Ideal
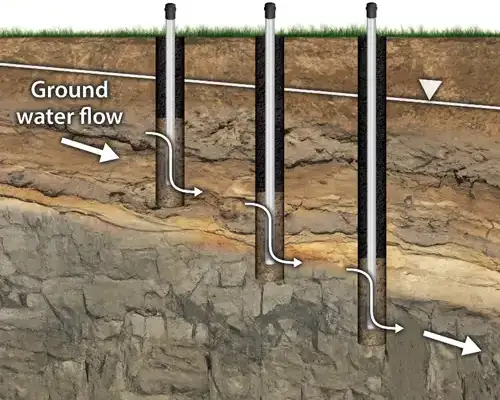

Arrows Indicate Groundwater Flow Direction
Installing well clusters can create ‘short-circuit’ pathways for water levels and chemistry across over-lapping sand packs.
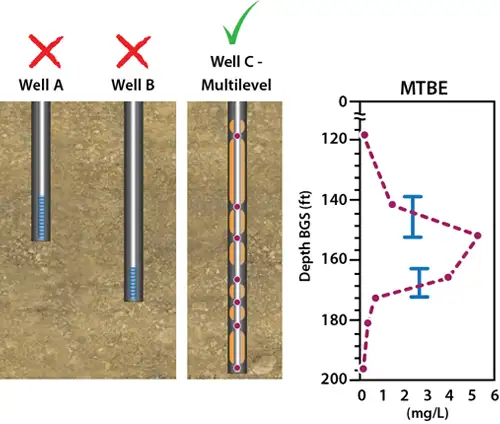
Long-screen wells can ‘over-estimate’ a contaminate thickness and ‘under-estimate’ the maximum concentration.
 Nested Wells – Not Ideal
Nested Wells – Not Ideal
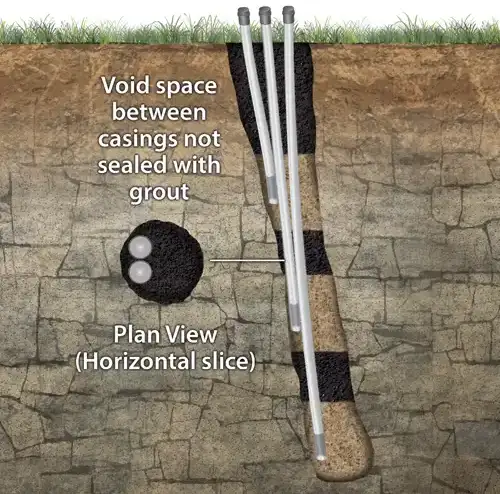
 Void space between casing not sealed with grout
Void space between casing not sealed with grout
Nested wells can also present biased chemistry and water levels at poorly sealed zones.
Multiple Level Wells Provide High Resolution Data
Creating ‘transects’ across zones of interest provides depth discrete data that can be compared ‘seasonally’ through various geological strata.
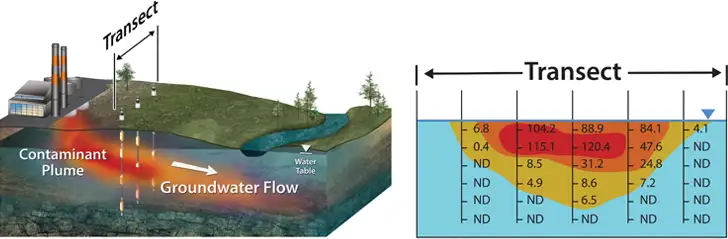
Image above showing Contaminant Plume Source and Groundwater Flow Direction. A Transect of Multilevel Systems Are Used to Monitor Detailed Contaminant Concentrations.
Multiple Level Well Case Study Examples
Planting 51 Trees Speeds Up Toluene Cleanup Efforts
High-Resolution Groundwater Data Proves Value Of CMT Systems In Botlek Area
Extensive Groundwater Monitoring Program At Refinery In Australia
Waterloo Multilevel Systems Help Characterize Plume In Landfill Expansion Project
19 CMT Multilevel Systems Successfully Installed In Challenging Geology
Flexible CMT System Adapted To Measure Submarine Groundwater
CMT Used To Measure Mass Flux At A Complex Site
CMT Ideal For Chlorinated Solvent Assessment
CMT Defines Vertical Gradients And Contamination At A UK Landfill Site
CMT System The Clear Choice For A German Air Force Base
CMT Bentonite Packers Used By AECL
Waterloo Multilevel Network Being Used To Characterize And Develop Remediation Strategy




